Nutrition for everyone, not just the sportsman, is likely one of the top vital parts of our well-being.
Sports meals are of utmost significance. Because consistent with health pros' research, to be wholesome, the diet bills 60-70%, and the exercise regime best money owed 30-40%.
Especially if you are a bodybuilder or often play prime-calorie sports like running, swimming, and vitamin, you will have to make a focal point.
When we work out for 90 minutes or extra or at an exceptional depth that requires numerous endurance, the body wishes a complete vitamin to maintain the method and get well briefly afterward. Here is a nutrition plan for athletes and those who work out much.

This article will cover which foods are great for our body, especially those who play muscle strength or endurance sports.
People who regularly exercise need to consume nutritious foods.
This article will synthesize and give you an overview of food for athletes you may not know yet. Now BellyFatZone invites you to refer to this article together!
1. What substances should sports players add?
1.1. Iron
Ordinary people need more iron every day; sports people need even more. When the body is active with great intensity, each cell needs an amount of oxygen many times higher than normal.
So the body also needs a corresponding amount of blood to the cells. An adequate iron supply prevents the body from worrying about iron deficiency anemia during sports activities.
1.2. Calcium
Calcium is one of the key ingredients that make up bones, so getting enough calcium will help prevent osteoporosis and minimize bone-related injuries during exercise. Some foods for sports players contain calcium, such as dark vegetables, seafood, nuts….
1.3. Magnesium
Similar to calcium, magnesium helps you build strong bones from the inside.
Besides, magnesium is involved in muscle movement – part of the contraction and relaxation of muscles – so the supplement is adequate to help the body function better than usual. You can take magnesium supplements
1.4. Fat

Fat provides more energy for players and helps provide essential fatty acids that the body cannot synthesize, such as omega 3 or omega 6. At the same time, it also helps the body transport fat-soluble vitamins.
1.5. The protein
Nearly every activity of the body requires protein, also known as protein. For those who are athletic a lot, being active requires more protein than usual to help the body repair tissues to produce antibodies to fight infections.
1.6. Carbohydrates
Also known as carbohydrates – it is one of the main sources of energy for people who play sports and exercise a lot.
Read more: Carbs Post-Workout – Expert Advice You Should Know.
1.7. Vitamins groups
Muscle cells always need many important vitamins, such as A, B, and C, to stay active during exercise. Therefore, for those who exercise a lot, adequate supplementation of vitamins is essential and important.
2. Food for sports players
2.1. Egg
For a long time, people attributed eggs as the cause of many people suffering from liver disease, heart disease, and high blood pressure. In the last 10 years, many scientific studies have shown that cholesterol in egg yolks is not as harmful as many people think.
The average person eating an average of about 2 fruits/day (14 fruits/week) also does not suffer. Bodybuilders can eat 2-3 eggs with yolks/day and 4 whites by boiling or beating to roll.

Eggs are relatively inexpensive, rich in protein, and contain most minerals and vitamins. Each egg usually contains about 5-6g of protein and 60 calories.
The amount of protein in eggs is considered the protein with the highest biological value of any food. This also means that the proteins in eggs are used most effectively for muscle growth.
The cholesterol in the egg yolk actively supports the body's production of steroid hormones, and ½ grams of leucine in each yolk is considered the ignition of muscle growth.
Eggs are the number one food for every athlete. You can quickly and easily prepare delicious egg-based meals every day.
2.2. Lean beef
Beef: Nutritional ingredients in beef include: protein content: 36 / 100g, 199 calories, carbohydrates: 0g.
Beef, especially beef, is rich in ammonia acid, higher than any other food, effectively building muscle, especially enhancing body health.

Beef is wealthy in vitamin B6 and protein: Beef has a large amount of vitamin B6 and protein, so it should be more suitable for nutrition.
Beef incorporates sufficient vitamin B6 that can help you construct immunity and protein to assist in metabolizing and synthesizing meals, contributing to the body's recovery after excessive tasks.
Beef has the mineral Carnitine, and the concentration of sarcosine (a substance connected to most cancers) is poor. Carnitine is mainly used to enhance fat metabolism and amino acid chains to keep the body in steadiness; amino acids are suitable for developing muscle.
Pork incorporates many minerals reminiscent of protein and potassium; those two minerals are indispensable in bodybuilders' diets. Low potassium ranges inhibit protein synthesis and enlargement hormone production, which affects muscle enlargement.
Oily beef: Low fatty acid content in beef, but rich in synthetic linoleic acid, effective against antioxidants capable of developing when exercising like weightlifting. Tissue.
Besides, linoleic acids may also be involved in muscle maintenance.
Beef is rich in magnesium and zinc: Magnesium and zinc contribute to protein and antioxidant synthesis to promote muscle growth.
Salts of glutamic acid, vitamin B6, and zinc interact with each other to strengthen the immune system and, more importantly, increase insulin metabolism's efficiency.
Beef contains a lot of vitamin B12: Vitamin B12 is essential for cells, especially red blood cells, to carry oxygen to muscle tissue.
Vitamin B12 promotes branched-chain amino acid metabolism, providing the body with vital energy during intense activities.
Also, the proteins in beef contain many amino acids and nitro-based acids. They will help convert the protein in food into organic sugars for daily activities. Besides, beef contains linoleic acid and palmitoleic against cancer and other soft diseases.
2.3. Sea fish

Once you want to gain muscle effectively, you need to think about fish, and fish is really the number one food you can not compete with. For example, in 100g of salmon, you can get 25g of protein and many other healthy nutrients.
Salmon is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, proteins that help reduce cholesterol and support the heart. For sports players, omega-3 fatty acids perfectly protect the heart system, reducing stroke when playing too hard.
Besides, omega-3 fatty acids reduce the risk of protein breakdown for muscles after exercise and improve muscle recovery.
This is important because, to build muscle, the body needs to store new protein faster than the old protein is lost.
Even if you practice hard but do not add food properly, the exercise's effect will not be promoted. Regularly eating salmon helps to tone muscles and boost metabolism.
In European-American countries or cold seas, they often eat salmon, sturgeon, cod, or tuna. Meanwhile, we can choose mackerel, scad, tuna, marine fish or pangasius, red carp, and snakehead fish, freshwater fish.
2.4. Chicken
Eating 100g of lean chicken will give you an extra 31g of protein with only 4 grams of fat.

Due to the high protein and low-fat ratio, if you eat a lot of chicken, you have a chance to build muscle mass.
You should combine chicken processing to create great-tasting dishes and diversify meals to get energy from this muscle-building top food.
Chicken breast contains up to 33g of protein content in 100g. This is the part that provides the most protein of the chicken, then the thighs.
So choosing chicken breast as a source of muscle protein is right.
The protein content and the complex amino acids in chicken positively affect the brain, improving mood, reducing anxiety, and stress, and improving blood pressure and heart rate. The average person needs at least 450g of chicken/per week.
Not only the nutrition, delicious taste, easy-to-eat, and easy-to-cook chicken meat has made chicken a favorite staple dish for sportspeople looking for protein supplementation—muscle strengthening.
Many people like to eat chicken with skin rich in fat.
If you are just an amateur bodybuilder, you can still eat chicken with skin, but it's best to grill them to remove the fat while ensuring delicious, crispy skin. Chicken is also a cheap source of protein compared to beef and pork.
2.5. Avocado
For those who play sports, cardiovascular health is the top concern. Avocado is like a fiber-filled ball, about 13 grams per fruit.
People who want to build muscle on a high-protein diet can add fiber to their meals because this is the key to a muscle-building diet.
Avocado is also a great source of heart-healthy unsaturated fats. Using a few butter slices with cookies or adding it to your salad is not a bad suggestion.
2.6. Nuts

Cashew nuts, peanuts, pumpkin seeds, pistachios, almonds … are all types of nuts that contain good body fat and provide significant calories.
Another important thing when eating oily nuts is that it helps you reduce the feeling of hunger in your stomach, especially for overweight people who want to train to tighten sharp muscles.
Therefore, oily seeds are ideal foods to snack on before and after each training session.
Walnuts and almonds are good sources of protein, fiber, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids.
They are also muscle-strengthening miracles, are easy to carry as a snack, and are healthy, unlike many other snacks.
Nuts also contain vitamin E, potassium, zinc, magnesium, minerals, and other essential vitamins.
They are also rich in fiber which aids in digestion. When buying nuts, avoid all deep-frying or salt-coated recipes. Try to buy the coarsest and least processed nuts if possible.
View more: Low-Calorie Density Foods
2.7. Olive oil
The monounsaturated fats in olive oil help increase male sex hormones, thereby promoting muscle regeneration. So for athletes who want to have toned muscles, the addition of olive oil in their daily diet will be perfect.
In contrast, some women who play sports to get a healthy body should not add too much olive oil to food.
2.8. Mineral water
Being active and playing sports always causes the body to sweat and lose water. Sufficient and timely replenishment of mineral water is always one of the top priorities.
During the training process, water is absolutely indispensable. Everyone knows water is important, but no one cares much about it. When you reach a certain muscle size, water helps to keep muscles going smoothly.
Just 8 glasses of water a day is enough for the exercise. You may be bored with drinking pure water so that you can replace it with other drinks. Try juices and smoothies to change the taste.
2.9. Green vegetables
Vegetables can easily be overlooked in a general fitness or sports diet. When you focus too much on protein, carbs, and high-calorie foods, vegetables are often pushed aside.

Bodybuilders need vegetables for phytonutrients and antioxidants. They help you fight disease, recover quickly, repair muscle and reduce hunger. Here are some of the vegetables that bodybuilders should eat:
Kale: The following is true of dark green leafy vegetables in which kale is a typical food. Kale is an excellent source of nutrients, rich in fiber, and copper, a source of nutrients that are difficult to obtain in a normal diet.
It is also a rich source of manganese, iron, vitamins C, A, and K, and various other phytonutrients. If you're wondering what to do with this green leafy vegetable, you can fry it or steam it like spinach.
Even easier, take the leaves and serve as a salad. Before you buy a bunch of lettuce, you need to be clear; the greens are not the same. Choose a dark green color, and you will reap more nutritional value due to the fiber and nutrients.
Sweet potatoes: Sweet potatoes come in many forms, with white to purple flesh, white skin, pink, brown, black. But they are all rich sources of vitamin C, manganese, fiber, vitamin B6, and other vitamins.
Sweet potatoes are also rich in potassium, a mineral that is good for the heart, helps keep blood pressure at normal levels, and helps prevent muscle withdrawal. Plus, sweet potatoes are a great source of complex, long-lasting carbs.
Beetroot: In exercising and exercising with gym equipment, problems of muscle fatigue and joint pain cannot be avoided. Beetroot is very effective in relieving joint pain and muscle fatigue.
If you don't want to eat, apply it directly to the wound. According to the survey of many athletes, about 80% use beet juice or sugar beet extract products.
There must be a reason for the beetroot to be so popular. The sugar beets' substances help transmit oxygen and nutrients to the muscles faster.
Besides, the nutrients in radish help promote and support the digestive system. The fiber in this food also promotes the absorption of zinc and minerals, assisting people with ulcers and inflammation of the stomach lining in food digestion.
If you have trouble drinking beetroot juice, you can consume it in many ways.
2.10. Bananas and fruits
Banana food is indispensable for sports players
Bananas are rich in the “quick response” carbs you need after a strenuous workout.
This type of carbs not only provides quick energy for you and is easy to digest, helping the body restore glycogen levels and rebuild damaged muscles. Besides, bananas also provide a lot of potassium the body needs during sports.
Bananas are one of the fruits with the most carbohydrates. Eating bananas for breakfast can help your body store the glycogen found in muscles and prevent muscle degeneration.

You can also grind a banana into a cup of post-workout protein water to replenish your muscle stores. Bananas are also rich in potassium, an essential electrolyte that helps in proper muscle contraction while strengthening the brain, enhancing memory, and supporting and calming the nervous system.
Pineapple: Pineapple contains the enzyme bromelain, a natural anti-inflammatory that helps restore bruises, sprains, and swelling. Besides, pineapple is also rich in vitamin C – an important component in tissue regeneration.
Kiwi: Just a small piece of kiwi will provide you with a large amount of vitamin C and potassium. Kiwi fruit is also rich in antioxidants, helping to soothe muscle aches.
One more thing to note is, do not throw away the kiwi peel, as the peel also contains many nutrients! I asked 10 people wishing to increase muscle with fruits containing vitamin C, and most of them mentioned oranges.
In fact, kiwifruit contains a higher content of these antioxidants than oranges, which can help you cut off body fat.
Scientists at Arizona State University have shown that vitamin C deficiency can reduce fat burning during exercise because vitamin C is essential for the synthesis of carnitine, a required molecule. In the proper oxidation of fatty acids.
Studies have also shown that the antioxidants present in kiwi help firm skin and slow down wrinkles' formation. Vitamin C and vitamin E are special antioxidants that keep the skin away from the attack of free radicals.
Blueberries: These lovely blueberries have excellent antioxidant effects. Many studies also show that blueberries can 3 times increase your recovery rate after heavy exercise.
Orange juice: Instead of energy drinks or sports drinks, choose a glass of orange juice.
It provides more vitamin C, but orange juice also adds to you much more potassium than sports drinks. Meanwhile, potassium is an important electrolyte that helps regenerate body fluid levels.
Apples: An apple a day will help you get rid of your fat waistline. According to data from a preliminary study, a compound in apple peel called ursolic acid may promote fat burning and increase muscle and bone mass.
With a lower sugar index than many other fruits, apples are ideal for pre-workout sipping. However, you should consider eating apples with the skin because, according to the Environmental Working Group, apples were found to have more pesticide residues than other fruits.
Avocado: Avocado is like a fiber-filled ball, about 13 grams per fruit. People who want to build muscle with a high-protein diet can add fiber to their meals because this is the key to a muscle-building diet.
Avocado is also a great source of heart-healthy unsaturated fats. Using a few butter slices with cookies or adding it to your salad is definitely not a bad suggestion.
Watermelon: This refreshing fruit is a rich source of citrulline and amino acids involved in nitric oxide production (NO).
Bodybuilders always know the importance of NO because it helps push blood through the muscles, allows the transport of nutrients, and assimilates restorative substances.
Studies show that citrulline can help relax and dilate blood vessels better than medications.
Read more: What Kind Of Food Bulking Meal Plan On a Budget?
2.11. Bread
Bread provides the body with a good amount of carbohydrates to help the body maintain energy, avoid muscle loss, and avoid fatigue when playing sports for a long time.
So before playing sports for about 30 minutes, you should eat some bread to avoid exhaustion and avoid cramps when exercising with vigorous intensity or a too long time.
2.12. Dried fruit

Dried fruit is one of the most energetic snacks and is great for athletes because it provides the body with a beneficial amount of natural sugar and many minerals.
Potassium and magnesium are essential – two minerals that are essential for regular sports players.
2.13. Whey Protein
Whey Protein is a cow's milk product when butter, cream, and protein are extracted in the cheese-making process or separated for protein.
Whey Protein is usually packaged as a nutritional powder in large jars or bags, and users dissolve it with warm water, milk, or juice to form a liquid food.
100 g of whey powder contains 80-90% protein; it is considered the “golden food” for general athletes and bodybuilders to restore, rebuild, and build muscle.
Today, whey protein is not far from everyone; not only in the gym, but almost middle-aged people also need a protein supplement to maintain toned muscles; whey protein is often imported in the form of a pot of 2.3 kg or 4.5 kg.
An amateur bodybuilder a month only needs to use a 2.3kg jar of whey protein to supplement protein; it is not too expensive compared to the great efficiency and convenience that it brings.
In particular, if you need weight improvement and want to add a large amount of Whey protein. More whey protein.
3. Food for athletes

3.1. Stir-fried beef with peas
A simple dish is easy to make, but it also helps to rebuild muscles for the body and provides energy for the body to operate more endlessly and supple.
Making:
- Thinly sliced beef and marinated with seasoning seeds, pepper, cooking oil, ginger, and garlic.
- The peas are washed and blanched with boiling water.
- Fry the garlic with cooking oil and then quickly add the beef to the island over high heat; then add the peas and fry it until the meat and beans are just cooked, then turn off the heat.
- For a plate, add some pepper and eat it hot.
3.2. Whey protein egg shake
This kind of milk may seem a bit too big because you have to use raw eggs, but it will be extremely safe and delicious.
Resources:
- Three eggs
- 2-3 scoops of vanilla ice cream
- 1-2 scoops of whey milk
See also: how to make delicious whey protein, rich in protein for the gym.
3.3. Bread slices with butter and nuts
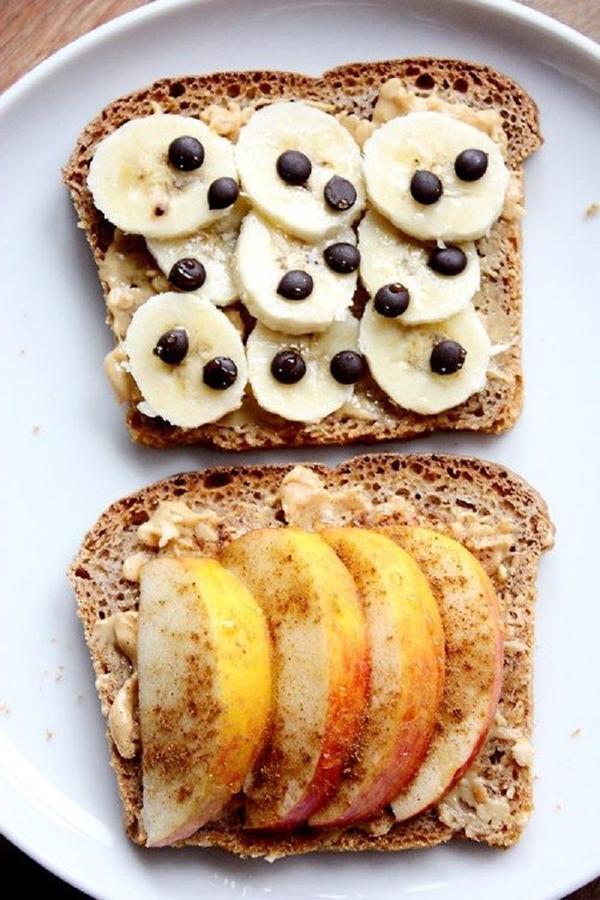

Depending on each person's preferences, choose different nuts such as cashews, squash seeds, almonds, and walnuts …
With this dish, you can eat about 30 minutes to 1 hour before training to provide the body with the number of carbohydrates and minerals needed for the movement.
3.3. Fresh orange sauce salmon
It not only helps to gain muscle and restore health quickly, but this is also a strange but equally attractive dish.
Making:
- De-fishy salmon by soaking it in fresh milk for 30 minutes, then rinse, and drain.
- Marinate the fish with any desired seasoning and then wrap the fish with a layer of cornstarch.
- Fry the fish until well done, add oyster oil and soy sauce to a dish.
- Add water to dilute cornstarch on the stove to stir to see the ripe flour, then turn off the heat for fresh orange juice and parsley to stir.
- Sprinkle the sauce on the fish plate, sprinkle with a little pepper and eat hot.
3.5. Salad with chicken breast, egg with yogurt sauce
It is one of the delicious and nutritious dishes for sports players and those who pursue a healthy, scientific diet.
Making:
- Making the soup: for all the ingredients, including honey, olive oil, salt, pepper, lemon juice, and unsweetened yogurt, mix well.
- Choose vegetables to make salad depending on each person's taste, add the boiled chicken breast, shred the small fibers, and mix well with the sauce.
3.6. Vegetable soup
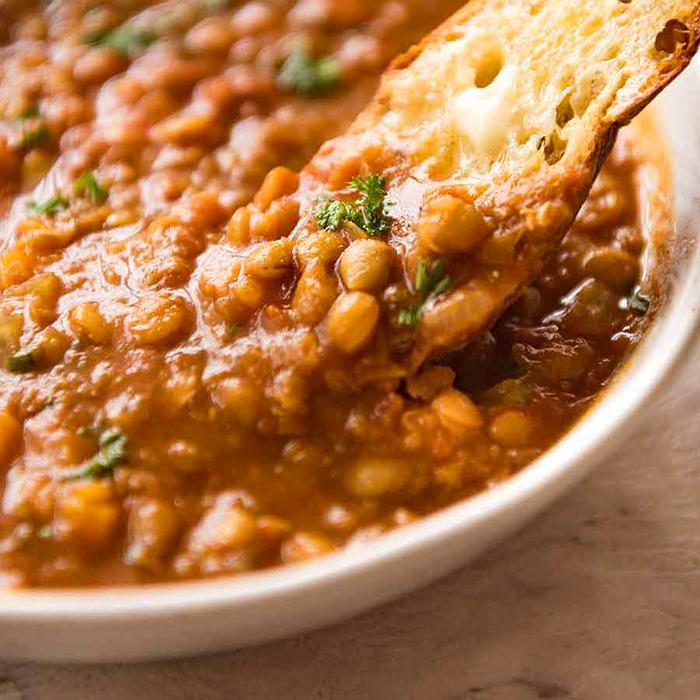

Help provide water and compensate for mineral salts lost to the body during sports.
Making:
- Depending on your preference, choose different types of vegetables to cook soup.
- After preliminary processing, the ingredients are put into a pot of cooking water (the order of cooking depends on the type of vegetable)—seasoning to taste.
- Finally, mix the cornstarch with a little cool water, put it in a pot of vegetables, and stir until it is thick.
4. Diet for sportspeople
A well-balanced diet can help athletes and gyms get the calories and nutrients they need to energize daily activities, including regular exercise.
Having a diet that boosts your fitness performance isn't as simple as choosing what to eat on the table. You need to eat the right foods at the right time of day.

The average person needs 2200-2500 kcal/day, sports players need from 2800-6000 kcal/day depending on the subject, or in other words, depending on the intensity and duration of training of each subject, specifically. :
- Those who practice weightlifting, athletics, art gymnastics need 2800-3000 kcal/day.
- Those who play “heavier” subjects like soccer, long-running, tennis, wrestling … need 4500-5000 kcal/day.
- Cyclists or climbers need 5000-6000 kcal/day.
Here are some general dietary considerations that sportspeople should know about:
- Eat varied: Sports foods need to be complemented by many different groups of nutrients. Eat a variety of plant and animal foods at each meal. The menu should be constantly changed to avoid duplication.
- Pay attention to water: If not promptly replenished to replenish the water lost due to sports, it is easy to cause muscle contractions, cramps, and dehydration, even life-threatening.
- The principle of not hungry, not full: You should eat a few snacks about 20-30 minutes before training because:
- If you exercise a lot while you are too hungry, you will quickly become tired, exhausted, or even faint.
- If you are too full, it will cause stomach upset and stomach prolapse.
- Vitamin balance: Supplement enough vitamins to help the body recover faster after exercise and avoid injuries caused by fatigue.
- Ensure enough energy: You should carefully calculate the amount of energy you have consumed and base it on the amount of energy in each dish that you have loaded to compare whether it is enough, not so moderate.
4.1. Before and during practice
Athletes and fitness enthusiasts are always looking for ways to improve their performance and achieve their goals. Good nutrition can help your body function better and recover faster after each training session.

The optimal amount of nutrients before exercise, exercise not only helps you maximize performance but also minimizes damage to muscles.
Fueling your body with the right nutrients before exercise will help you get the energy and strength you need to perform a better workout.
Each macronutrient has a specific pre-workout role. The proportion of substances to be consumed will vary with individuals and with each type of exercise.
4.1.1. Carbohydrates in pre-workout nutrition
Our muscles use glucose from carbohydrates for fuel. Glycogen is the major form of glucose storage in the liver and muscles.
For short and intense exercise, the body's glycogen stores will be the main source of energy for muscle movement.
But with longer exercises, the level of carbohydrate usage will depend on the intensity, type of exercise, and overall diet. The muscle's sources of glycogen stores are limited. When the reserves become depleted, your mobility will decrease.
Studies have shown that carbohydrates can increase glycogen storage and utilization while promoting carbohydrate oxidation during exercise.
4.1.2. Protein in pre-workout nutrition
Numerous studies have noted the potential of pre-exercise protein consumption to improve athletic performance.
Eating protein before exercise has been shown to increase muscle protein synthesis. There are also many benefits of eating protein foods before exercising, such as:
- Muscle growth.
- Improve muscle recovery.
- Increases strength and body mass.
- Increased muscle performance.
Adequate protein intake before exercise
4.1.3. Fat in pre-workout nutrition

Glycogen is used for short and high-intensity exercises. Fat is the source of energy for long, medium, and low-intensity exercise.
One study found that a four-week diet with 40% fat increased running time in healthy runners.
4.1.4. Water
Our bodies always need water to function. Water has been shown to help maintain and even increase performance. While dehydrated, there will be a significant decrease in exercise performance.
It is recommended to use water and sodium before exercise; this will help the body balance fluids.
The American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM) recommends drinking 0.6 liters of water 4 hours before exercise. Drink 0.5 liters of water for 10-15 minutes before exercising.
4.1.5. Time of meals before training
To maximize exercise results, try to eat a complete meal containing carbohydrates, protein, and fat 2-3 hours before training.
However, in some cases where your time doesn't work, you can just eat a meal closer to your workout time. However, you need to know that the closer you eat to the time of practice, the smaller and simpler the meal should be.

If you eat 45-60 minutes before exercise, choose simple foods that are easy to digest and contain mainly carbohydrates and protein. This will prevent stomach discomfort during exercise.
Some examples of pre-workout meals:
- Workout starts in 2 – 3 hours or more:
- Sandwich with whole grain bread, lean protein, and salad.
- Eggs and whole-grain toast topped with butter and a cup of fruit.
- Lean protein, brown rice, and grilled vegetables.
- Workout starts within the next 2 hours:
- Protein smoothies are made from milk, protein powder, bananas, and berries.
- Whole grains and milk.
- One cup of oatmeal, banana, and almonds.
- Natural almond butter and fruit on whole grain bread.
- Workout starts within the next hour:
- Yogurt and fruit.
- Nutrition bar with protein
- A piece of fruit: banana, orange, apple, …
You don't have to eat a lot of pre-workout meals; just choose one of these.
4.2. After exercising
Consuming the right nutrients after exercise is just as important as what you ate before.
When you go to the gym or exercise, your muscles may have used up their glycogen stores for energy. This results in a lack of glycogen in your muscles. Along with that, some proteins in muscles are also broken down and damaged.
After exercising, your body will try to store glycogen and repair and restore muscle proteins.
Therefore, eating the right nutrients right after exercising can help your body get this job done faster, especially carbohydrates and proteins.
4.2.1. Protein, carbohydrates, and fats are involved in post-workout recovery
The protein

Exercise will trigger muscle protein breakdown. The rate at which you break down depends on the exercise and your fitness level.
Consuming an adequate amount of protein after an exercise provides the body with the amino acids it needs to repair and rebuild damaged proteins. It also helps to build new muscle tissue.
You should eat between 0.3 and 0.5 grams of protein per kilogram of your weight immediately after exercise.
Carbohydrates
The body's glycogen stores are used for energy during exercise, and the post-exercise carbohydrate supply replenishes these stores.
The rate at which glycogen stores are consumed depends on your activity. If you do endurance sports (swimming, running, etc.), you will need to consume more carbohydrates than a gym person.
A recommended intake of 1.1 – 1.5 g of carbohydrate per kilogram of body weight should be provided within 30 minutes of exercise for appropriate glycogen recombination results.
Fat
Many people believe that eating fat after exercise will slow digestion and inhibit the absorption of nutrients.
While fat can slow down the absorption of your post-workout meal, it won't diminish its benefits.
Time of post-workout meal
Post-workout meals should be eaten within 45 minutes of exercise. However, you can extend this time a bit longer, depending on how long your pre-workout meal is.
A few examples of quick and easy to eat after a workout:
- Grilled chicken with grilled vegetables.
- Scrambled eggs with butter spread on toast.
- Salmon with sweet potatoes.
- Sandwich: salad, tuna on whole grain bread.
- Tuna and crackers.
- Oatmeal, protein, banana, and almond.
- Cheese and fruit.
- Rice cakes and peanut butter.
- Whole grain water bread and almond butter.
- Cereals and skim milk.
- Yogurt, berries, and granola.
- Protein and bananas.
- Raw grain and peanut sandwiches.
Water

Especially, we cannot lack water, need to drink plenty of water before and after exercise.
During exercise, your body loses water and electrolytes through sweat. The replenishment of water and electrolytes after exercise helps the body recover and achieve peak performance.
Depending on your exercise's intensity, you need to properly replenish water and electrolytes with the amount lost during exercise.
5. Attention
5.1. Don't double the amount of meat
Many people who play sports because they want to gain muscle think to eat as much meat as possible, but according to nutritionists, they should only eat an average amount of meat.
Because even if you eat more meat, your body can not tolerate it anymore, and even increases the risk of heart.
5.2. Don't overdo sugar and sugary foods
In essence, everybody needs sugar, especially those who play sports regularly, but the overuse of foods containing sugar will lead to hypoglycemia. When you want to add sugar, you should prioritize foods containing natural sugars, such as some sweet fruits.
5.3. Don't Drink too much coffee every day

Drinking coffee can help you become more alert, active, and agile. However, depending on each person's body, only add enough coffee because if you drink too much, it will easily make you get drunk, making your heart beat faster, dizziness, nausea, headache …
5.4. Do not add protein in the form of a powder or medicine
After exercising, many people want to be toned and want to gain muscle quickly; they look for protein supplements in the form of powder or pills. In practice, however, this is ineffective because muscle gain is essentially the result of regular exercise, not necessarily the high protein intake.
6. 1-week menu for sports players
Here is a menu using foods for sports players to refer to build yourself a menu that best suits you.
| Breakfast | Lunch | Dinner | |
| Monday |
|
|
|
| Tuesday |
|
|
|
| Wednesday |
|
|
|
| Thursday |
|
|
|
| Friday |
|
|
|
| Saturday |
|
|
|
6. Functional foods for sports players
In addition to the healthy foods mentioned above, sports players can also add many functional foods that enhance vitality and nourish the body to make health more and more supple. , higher durability.
Some products sports players may be interested in such as strength enhancement, strength increase, electrolyte gel….
Superfoods For Endurance Athletes – Healthy Foods For A Balanced Diet

I hope this article's information helps you have more knowledge needed to use good food for athletes to support your practice; this will help you achieve maximum efficiency.
View more:
- Top 18 Good Fats For Weight Loss – To Have in Your Kitchen
- Is Vitamin C Good for Gym?
- List of Vegetables For Weight Loss for You to Add to the menu Every Day
Please share it if you find it helpful.