If you are one of the followers of eggs, this is the article for you; indeed, not only do you love to eat eggs, but many other people like you, eggs are an excellent food.
“What do you cook with eggs?” This is a question many people ask when preparing meals for themselves and their families. But besides the delicious variety of flavors, did you know that different cooking methods can affect the number of nutrients the body absorbs from eggs?
Studies show that choosing the right way to cook them helps optimize the nutritional value of eggs. Below we will explore each method in turn, look at their advantages and disadvantages, and finally rate them relatively on a scale of 1 to 5.
Let's explore with BellyFatZone!

But regardless of rating, always remember that eating eggs is always good for health, and even when there are nutritional differences, these recipes are straightforward to make.
What are the evaluation criteria?
To score these processing methods, we will rely on the nutritional value of eggs. As follows:
Amount of protein
Eggs are among the cheapest and most nutritionally valuable sources of protein, meaning the protein found in eggs is more efficiently absorbed and used by the human body, according to a review published in the Journal of Science Sports & Medicine.

Micronutrients
There are many micronutrients found in egg yolks. Eggs are a top source of B vitamins that fight belly fat along with choline. In addition, this is also one of the 20 best sources of selenium to help regulate metabolism, improve mood and immunity; vitamin B2 (riboflavin) helps the body metabolize energy and vitamin B12.
Depending on how the eggs are cooked, the content of these nutrients can be significantly reduced, so methods that retain more nutrients will score higher.
Excess calories
This is a matter of weight loss. Some cooking methods use fats such as oil or butter. Just one tablespoon of butter adds 100 calories to a meal. But if you don't care about the weight, you don't need to pay attention to the fat when cooking, choose the right kind of good fat.

Butter or extra virgin olive oil is ideal. A 2016 study published in the journal PLOS ONE found no link between avocados and heart disease. Extra virgin olive oil is rich in heart-healthy monounsaturated fats and antioxidants. Oxidation prevents disease.
In contrast, cooking eggs with vegetable oil increases the amount of omega-6 fatty acids, a group of fats that cause inflammation and increase waist circumference.
Now we will learn the different egg processing methods to see the nutritional value of the finished egg.
Eat raw eggs
Some people like to eat eggs raw, either plain or added to their milkshakes, to increase their protein intake while working out.

Advantages
Raw eggs contain higher levels of vitamin A than cooked eggs. According to a report published in the International Journal of Food Science and Nutrition, levels of vitamin A1 (also known as retinol, which is essential for vision, skin, and human development) in the cooked yolk are 20% less than in raw form.
However, there is no need to worry too much about this decrease, because according to the nutrition update of the US Department of Agriculture, “Currently, vitamin A deficiency in the general population is very rare.”
Defect
Increased risk of Salmonella infection (eggs must be heated to about 70 degrees Celsius to kill this bacteria) and only half the protein from raw eggs is absorbed by the body (compared to 91% in cooked eggs, according to a study published in the Journal of Nutrition).
In addition, raw eggs contain avidin protein that binds to biotin – a B vitamin that helps keep hair looking shiny. Avidin prevents the body from absorbing biotin, but it denatures avidin and makes it ineffective when cooked.
Scoring: 0/5
Raw eggs have more bad sides than the good side, so cooked is better.
Scrambled eggs (stirred eggs)
Method: Crack the eggs into a bowl and beat until the whites and yolks are combined; then, you can add water or cream. The beaten eggs are placed in a pan coated with butter or oil, usually over medium or high heat. Use a spatula to continuously stir the eggs in the pan until the eggs are cooked evenly.

Advantages
Adding a little water to the egg will create steam during cooking, making the egg lighter and softer. This allows both the yolk and the white to be eaten, and the quick cooking time also reduces the risk of loss of temperature-sensitive nutrients.
Defect
This method often causes the egg to overcook when the proteins bind tightly together. When the proteins squeeze closer together and overheat, it pushes the liquids out, pulling in some water-soluble vitamins, such as vitamin B12, one of the eggs' essential substances.
B12 is an essential vitamin found only in animal foods. One egg provides about 10% of the daily recommended amount of vitamin B12, and vegetarians are often susceptible to a deficiency of this vitamin, which can lead to inflammation and other health problems. Scrambled eggs are also usually cooked with a lot of butter, which increases the fat content.
Scoring: 3/5
Thoroughly boiled eggs
Here's how to boil eggs in boiling water for about 8 to 10 minutes. Such a long cooking time allows both the white and the yolk to solidify completely.

Advantages
This method is entirely fat-free and keeps the whole egg.
Defect
Sometimes a portion of the white is stuck to the shell when peeled, causing some protein loss, although not significantly. More importantly, a study in the Journal of Agricultural Food Chemistry found that the boiling method reduced the antioxidants in egg yolks the most – by 22.5%.
Specifically affected is lutein, a bioactive compound that helps maintain eye health. The cause of this loss may be due to the long cooking time.
Scoring: 3/5
Omelet
This is a very familiar dish, but almost everyone has a different way of making it. Americans, British and French have other dishes' techniques, be it country style or restaurant style, stuffing or empty, etc.
Either way, first beat the egg until it melts. Some people add water or cream; then the beaten eggs are poured into a pan with oil or fat; some keep the heat low, others support the heat high.
Some methods involve tossing the eggs around the pan to produce a partially cooked part first, while the liquid is cooked by lifting the edge of the omelet to let the juice run down the bottom. Once cooked, the omelet can be rolled or doubled.
Advantages
Eat the whole egg and can add more vegetables.
Defect
If you don't turn the eggs over, so the top is cooked, it may take longer to fry. In doing so, the heat-sensitive micronutrients contained in the yolk are easily lost significantly.
Scoring: 4/5
One-sided omelet
This is a “photogenic” method of preparation because the product has a beautiful sparkling golden yolk. Still, very few home cooks use this method because the top of the egg is not exposed to heat, so the white can be loose and unripe if not done correctly.
The chef's method is to crack the eggs in a non-stick pan with oil or butter and not flip. To make the top cooked, they can either spread the hot oil in the pan, let the heat simmer for a long time, or cover the pan to let the steam cook the eggs.
Advantages
This dish will retain all the nutrients found in the slightly raw yolk and use very little fat if done correctly.
Defect
Since eggs are not turned over, they may not be cooked enough to remove all harmful bacteria.
Scoring: 4/5
Poached eggs
This method uses no added fat to place the beaten egg in boiling water and sit for 4 to 5 minutes. This makes the whites just cooked and the yolks still liquid.
Advantages
Studies show that the protein in cooked egg whites is easier to digest because it has been denatured. Raw or slightly liquid yolks contain 50% more nutrients than well-cooked yolks.
Defect
To make this dish correctly, you must use fresh eggs of the best type with thick and firm whites; otherwise, when you put eggs in boiling water, it will create many white filaments that dissolve in water, losing the amount of protein compared to other methods is different.
Scoring: 4/5
Boiled (hard-boiled eggs)
Eggs in their shells are put in boiling water for 5 to 6 minutes, which is enough time to cook the whites while the yolks are still liquid thoroughly.
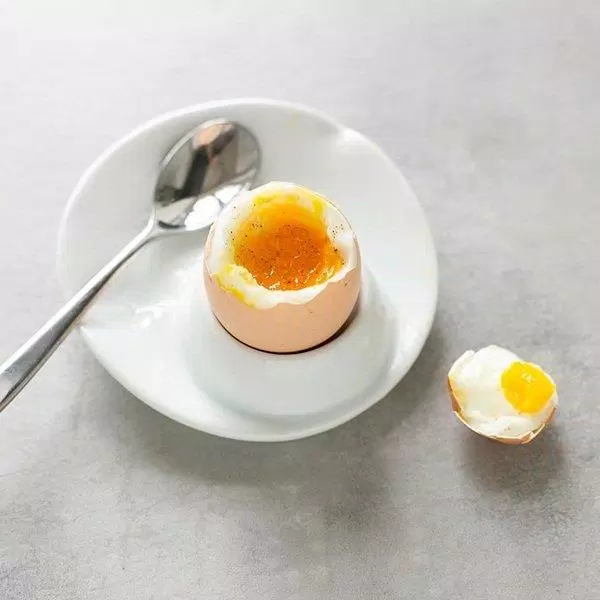

Advantages
Since it is also boiled, no extra fat is used and the whole egg is preserved. Since the yolk is still liquid, it retains many of the heat-sensitive nutrients.
Defect
The whites can stick to the shell and be challenging to peel.
Scoring: 5/5
This is a popular way to cook eggs because it contains few calories, the whites are rich in protein, and the egg whites are fully cooked but still retain the micronutrients in the yolks. Especially the taste of poached eggs is much more delicious than hard-boiled eggs or other methods.
Baked eggs
This is a whole egg or scrambled egg placed in a cup or cake mold and baked in the oven at about 175 degrees Celsius until cooked through. Some people like to add butter on top.

Advantages
You will eat the whole egg, and this method is straightforward because there is no need to cook on the stove.
Defect
Be sure to use extra fat to keep the eggs from sticking to the mold. In addition, prolonged cooking time can make eggs hard and reduce nutrition.
According to a study published in the journal Food Chemistry, when eggs were beaten and then baked in an oven at 175 degrees Celsius for 40 minutes, only 39 to 45 percent of the vitamin D was retained.
Meanwhile, frying or boiling eggs can retain 82 to 88% of vitamin D, a substance that boosts the immune system and improves mood.

Scoring: 2/5
Vitamin D is often lacking in our diets (most people absorb vitamin D through exposure to sunlight). The way eggs are baked, vitamin D leads to quite a lot of points lost.
Only eat egg whites
This way of eating is popular because US public health agencies have said that egg yolks can raise blood cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of heart attack and stroke. However, now experts have discovered that this is not the case.

The 2015-2020 US Dietary Guidelines have removed the 300-milligram limit of dietary cholesterol, asserting that current evidence suggests no link between dietary cholesterol and blood cholesterol levels. . Even eating eggs in moderation can help lower cholesterol.
Advantages
One egg white provides about 3 grams of protein (that's half of the whole egg's 6 grams of protein) and has only 15 calories, while the yolk contains 3 grams of protein and 60 calories. So when you omit the yolk, you can get the same amount of protein with fewer calories.
Defect
Egg yolks contain a lot of micronutrients and good fatty acids, including selenium, riboflavin, vitamin D, phosphorus, vitamin B12, folate, iron, vitamin A, vitamin B6, and choline that help prevent belly fat accumulation.
In addition, if you want to remove the yolk, you must break the egg; then, more fat must be used to process the white.

In particular, if you buy pre-made egg whites, they may contain unnecessary additives.
Scoring: 3/5
Since egg whites are high in protein and low in calories, they're still appreciated, but those calories can be offset by adding fat to cooking.
If you're on a diet and need to keep an eye on your calorie intake, you can use egg whites, but it's a good idea to eat a few extra yolks to get more nutrients found less in other foods like choline, selenium, and vitamin D.
For example, you can make scrambled eggs with 3 whites and 1 yolk for 120 calories less than using 3 whole eggs.
Soft omelet
This fried egg is made by beating the whole egg into a pan with a thin layer of oil. Before the underside of the egg begins to brown, you must turn the entire egg over so that the yolk is intact and cook the other side, resulting in the white being cooked while the yolk is still liquid.

Advantages
Flipping the egg makes the white less raw, meaning the protein is better absorbed by the body while keeping the yolk full of easily absorbed micronutrients.
Defect
Turning the egg upside down when frying causes an extra layer of grease on the dish.
Scoring: 3/5
Hard omelet
To make this dish, one will crack an egg into a pan and make the yolk break. Then the eggs are also turned over and left to cook entirely on the other side. So both the yolk and the whites are fully cooked.

Advantages
The whole egg can be eaten, both the yolk and the white.
Defect
When the yolk is cooked, the heat-sensitive antioxidants and nutrients can be significantly reduced. According to the Journal of Agro-Food Chemistry, eggs can lose up to 18 percent of xanthophylls when frying egg yolks. This carotenoid can scavenge harmful free radicals. In addition, the egg is also covered with a layer of grease when flipped.
Scoring: 3/5
Conclude:
If you've read this far, you already know how many dishes eggs can be cooked and the nutrient content of each dish from eggs.
You can choose the food that suits your taste and preferences so that you can both eat well and ensure your body's nutritional needs.
So you already know the different ways to cook eggs and the nutritional value of each method. What's your favorite way to eat eggs?






