Bone and joint health are essential for ordinary people but always important, especially for those who regularly practice sports and weight training.
The musculoskeletal system is the framework to support the body to keep the body healthy and move flexibly.
There are many products to support the joints, and one of the most popular products today is Glucosamine.
What is glucosamine? Glucosamine is a natural compound like cellulose, used by the body to create joint cartilage.

Glucosamine is available in the human body or supplemented from external foods.
Glucosamine's effect is to support bone and joint health, in the form of medicine also works to treat joint diseases.
In this article, we will learn about the benefits, dosages, and side effects of Glucosamine.
What is glucosamine?
When you're young, you may be less concerned about bone health. But if you do sports or get older, you will realize that a weak musculoskeletal system will cause many inconveniences.
Glucosamine is known as a substance that has a significant support effect on bones and joints. But actually, what Glucosamine is, how it works, do you understand?
What is glucosamine?
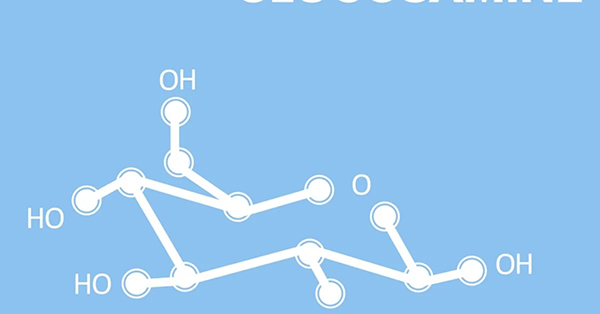
Glucosamine is a natural compound. By chemical classification, it is classified as an amino sugar group synthesized from glucose. What is glucosamine used for?
It has a cartilage-forming effect and is often used to treat and prevent osteoarthritis pain, such as arthritis.
Where is glucosamine?
Glucosamine is found in almost all body tissues, concentrated in connective tissue and cartilage tissue.
The human body has the ability to synthesize Glucosamine on its own, but this ability decreases as you get older. Therefore, supplementing this substance from external sources is essential.
Besides, where does Glucosamine come from? It is also found in some animals and non-human tissues, including shells, animal bones, and mushrooms.
Additional forms of Glucosamine are usually produced from these natural sources.
It can be supplemented with natural foods, taken as a pill, or applied as a cream.
View more: How to Start Taking Supplements?
Glucosamine's effects on bone and joint health
What is glucosamine, and why do we need to take it?
The next section will clarify its role in your body.
1. Relieves inflammation
Glucosamine is often used to treat symptoms of various inflammatory conditions. Although its mechanism of action is not known, reducing inflammation is noticeable through several scientific studies.
A test-tube study demonstrated the tremendous anti-inflammatory power of glucosamine when tested on cells involved in bone and joint formation.
Most Glucosamine studies involve simultaneous supplementation with Glucosamine with another compound similar to it, Chondroitin, which works to produce and maintain healthy cartilage.
A study of over 200 people using glucosamine supplement product lines decreased by 28% and 24%, respectively, for inflammatory markers: CRP and PGE.
However, these results are not entirely clear. Besides, a similar study found that people using Chondroitin reduced their inflammatory markers by 36%. This is a significant result.
Many studies support these findings. Remember, many people taking Chondroitin report that they also take glucosamine.
Therefore, it is not clear whether the results given above are from the Chondroitin test alone or are combined with Glucosamine.
In summary, the effectiveness of Glucosamine inflammation is still inconclusive. But many studies have shown it can reduce inflammation, especially when combined with Chondroitin supplements.
2. Support joint health
Glucosamine naturally exists in the body. And one of its main roles is to support the healthy development of tissues between your joints.
Cartilage is a white tissue that covers the ends of bones where they meet and form joints.
This tissue, together with a lubricating fluid called synovial fluid, allows the bones to move freely through each other, minimizing friction to help prevent pain during movement.
- So what role does Glucosamine play here?
It helps form several chemical compounds involved in creating joint cartilage and synovial fluid.
Some studies show that Glucosamine can protect joint tissue by preventing cartilage breakdown and reducing collagen degeneration.
A study of 41 cyclists found that supplementing with 3g of glucosamine daily reduced collagen loss in the knee joint by 27%, compared to only 8% in the normal eating group.
Another small study also found a significant decrease in collagen breakdown rates, with collagen synthesis rates in the articular cartilage of footballers being given 3g glucosamine daily for 3 months.
3. Treatment of osteoarthritis pain
It is also being researched and used to treat various bone and joint problems, such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoporosis.
Many studies have shown that daily glucosamine supplementation is a long-term, effective solution for knee osteoarthritis by reducing pain, maintaining the cartilage layer, and slowing down the disease's progression.
However, the use of Glucosamine in the form of medication should be done by doctors; you should not use it independently.
Also, Glucosamine is thought to work for many other ailments, but so far, there is no convincing scientific basis.
Its benefits for osteoarthritis are the most convincing and are being widely used.
4. Bladder pain
Glucosamine is widely used in treating bladder pain (IC), a symptom associated with Glycosaminoglycan deficiency.
Because glucosamine is the premise of this compound, theoretically, glucosamine supplementation through products may also help control IC.
However, more research is needed to conclude.
5. Inflammatory bowel disease
Like bladder pain, intestinal inflammation is also associated with a deficiency of Glycosaminoglycan. Currently, there is little scientific evidence that glucosamine can help treat inflammatory bowel disease.
6. Multiple sclerosis
Many sources recommend that glucosamine can be an effective treatment for multiple sclerosis.
However, more research is needed. One study evaluated glucosamine efficacy in addition to traditional treatments for multiple sclerosis.
7. Beaded water
Many believe that using glucosamine can aid in the treatment of cataracts.
A few studies have shown that glucosamine can increase vision health by reducing inflammation and enhancing antioxidants in the cornea.
However, much larger studies are still needed to confirm this information.
Is glucosamine really good?
Although there has been much publicity about the positive effects of glucosamine on treating many diseases, studies only support its effects in a small therapeutic scope.
The most evident evidence supports the use of glucosamine in the long-term treatment of knee osteoarthritis symptoms. This means it may not work for everyone.
According to available data, this is definitely not an effective treatment for other diseases and inflammatory symptoms.
If you intend to use glucosamine, pay attention to the quality of the supplements you choose, as each disorder will be different and give a different effect.
Ideally, you should still consult your doctor if possible!
Glucosamine supplementation like?

You can get more Glucosamine through the body in two ways: natural foods or supplements.
1. Natural food
Cartilage, rib cartilage of cow, chicken, duck, pork, shells of seafood such as shrimp, crab …
Besides, young people also have the ability to synthesize Glucosamine from glutamine-rich foods like beef, lamb, chicken, fish, eggs, milk, beans, and green vegetables.
2. Food supplement
Glucosamine oral tablet has not been recognized as medicine but only as a supplement. In this form, Glucosamine has 2 types:
- Glucosamine sulfate
- Glucosamine hydrochloride
Sometimes, glucosamine sulfate is also sold in combination with chondroitin sulfate. Most of the scientific data showing the highest efficacy are Glucosamine sulfate or Glucosamine sulfate combined with Chondroitin.
Side effects of Glucosamine
Some of the unwanted symptoms that can occur when you use Glucosamine oral tablets are:
- Nausea, vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Heartburn
- Stomachache
- Asleep
- Headache
The above symptoms may be encountered when you overdose or in the early stages when the body is not used to it.
Try reducing the dose; if the symptoms still do not decrease after some time, you should stop taking and consult a doctor.
Also, if you experience any unusual symptoms when using the product, consult your physician or pharmacist.
Who should use Glucosamine tablets?
- Older adults, bone and joint health decline
- People suffering from osteoarthritis for a long time (if using treatment need a doctor's prescription)
- People with weak bones and joints
- People don't eat enough food.
Who should not use a glucosamine supplement?
Glucosamine is safe for most people. However, if you belong to one of the following subjects, you should use caution; it is best to consult a qualified person.
- People under 18: How old is glucosamine? Use when you are over 18 years old.
- Pregnant or lactating women: There is no evidence of the safety of Glucosamine on this subject.
- People preparing for surgery or bleeding disorder: Glucosamine may increase bleeding risk in many cases.
- People allergic to seafood: Some Glucosamine products have ingredients from the tail, and shells of seafood. You should carefully study the ingredients before using them.
- People with diabetes: This substance can interfere with blood sugar control for people with diabetes, although this risk is relatively low. If you have diabetes or are taking medication for diabetes, talk to your treating doctor about using Glucosamine.
- People with flu, ear, nose, and throat disease: Be careful when using this oral tablet.
How to take Glucosamine correctly?
1. Glucosamine how to drink?
This product is usually in pill form; you take it with water, similar to taking medicine. Also, to increase absorption efficiency, you should drink plenty of water.
Glucosamine supplements are all made from natural sources, including shells of seafood or mushrooms, or artificially produced in the laboratory.
Glucosamine supplements are available in two forms:
- Glucosamine Sulfate
- Glucosamine Hydrochloride
Typically, manufacturers sell products containing Glucosamine Sulfate separately or combined with Chondroitin Sulfate.
2. How many capsules are taken on Glucosamine?
- The dosage of each pill will vary by manufacturer. You should carefully read the use instructions on the packaging or, as directed by your doctor, do not exceed the allowed dose.
- Typically, Glucosamine is taken at 1,500mg per day.
3. Glucosamine drink morning or evening, before or after eating?
You can use the product all morning or evening, preferably during or immediately after a meal.
4. How long does Glucosamine take to work?
This is just a supplement, not a drug, so you will hardly see the effect immediately. Usually, after 2-3 months of use, you will notice a positive change in your joints.
Also, to achieve the highest efficiency, you should combine exercise, sports at moderate intensity.
Glucosamine good kind?

There are many Glucosamine supplements available in pill form to choose from. Please trust the products of reputable brands to ensure effective protection and safety.
Blackmores is the leading health food and supplements brand in Australia.
Glucosamine Sulfate 1500mg One-A-Day support pill of the company is currently the most popular product today, with the effect of reducing joint pain caused by arthritis, and increasing mobility.
The above article has provided all information about Glucosamine, its effects, side effects, and effective supplements.
Take care of your bones and joints right now by eating healthy foods, exercising regularly, and taking additional foods if needed.
It is better to combine Glucosamine and Omega 3 Fish Oil to support joints and heart health!
Benefits of Glucosamine Video:
Best Selling Glucosamine Combination Nutritional Supplements:
Read more:
- Insulin? Eating Frequently and Insulin – Mechanism of Action of Insulin
- Herbalife Weight Loss Diet Plan Effective, You Should Know!
- Benefits of Casein Protein Powder and How to Use it Effectively
References
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/D-glucosamine
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17270442
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19724889
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22434264
Hopefully, the information above has helped you choose “glucosamine benefits,” bringing some small value to you: “Save Your Time” and give it to training. Please share this article if you feel it is functional. Thanks!






